Understanding Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian cancer begins in the ovaries, the two small, almond-shaped organs that produce eggs and hormones in women. It’s a complex disease with various subtypes, each having its unique characteristics and treatment options. The two most common types are epithelial ovarian cancer and germ cell ovarian cancer.Risk Factors
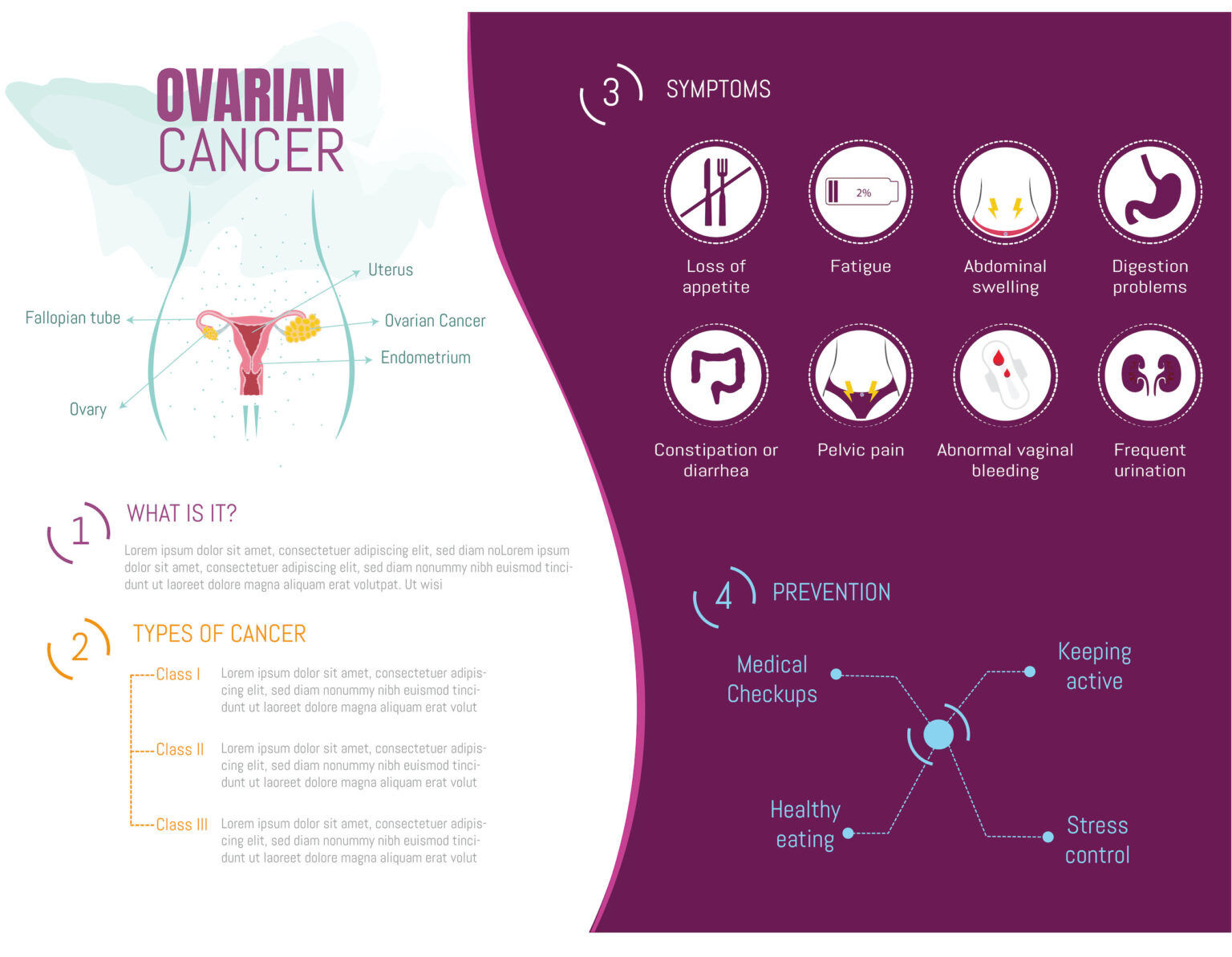
Several factors can influence the risk of developing ovarian cancer. Age plays a significant role, with women over 50 facing an elevated risk. Genetic factors, particularly a family history of ovarian or breast cancer involving BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutations, can also increase susceptibility. Reproductive factors, such as never having been pregnant, giving birth at a later age, or experiencing menopause after 50, contribute to a higher risk. Prolonged use of Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) may slightly elevate the risk, while women with endometriosis face an increased likelihood of certain ovarian cancer types. Obesity is another contributing factor, and although the link is inconclusive, some studies have suggested a potential association between talcum powder use in the genital area and ovarian cancer. Understanding these risk factors is vital for early detection and prevention.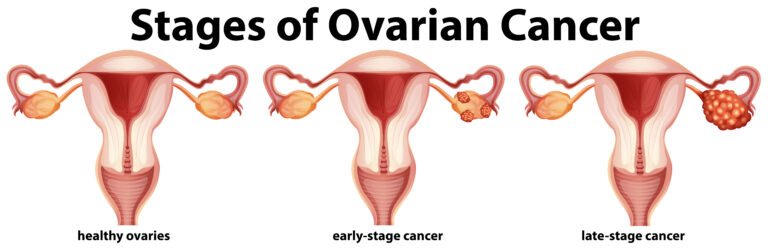
The Importance of Early Detection
Ovarian cancer is often referred to as the “silent killer” because its symptoms are vague and easily overlooked. Common symptoms include bloating, abdominal pain, feeling full quickly, and changes in bowel or bladder habits. Unfortunately, these symptoms are often mistaken for other less severe conditions, leading to late-stage diagnoses. Early detection is key to improving survival rates. When ovarian cancer is caught in its early stages (stage I or II), the 5-year survival rate can be as high as 90%. However, at stage III or IV, when the cancer has spread to other parts of the body, the survival rate drops significantly. To promote early detection, women should be aware of their bodies and any changes that may occur. Regular gynecological check-ups, including pelvic exams and ultrasounds, can help identify potential issues. Moreover, genetic testing for high-risk individuals can provide valuable information about cancer susceptibility.Prevention and Awareness
While there’s no surefire way to prevent ovarian cancer, there are steps women can take to reduce their risk:
Oral Contraceptives: Some studies suggest that long-term use of birth control pills may reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Having children and breastfeeding can lower the risk.
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and a balanced diet may help reduce the risk.
Family History: If there’s a family history of ovarian or breast cancer, consider genetic counseling and testing.
Awareness: Ovarian Cancer Awareness Month provides an excellent opportunity to educate yourself and others about the disease. Share information, attend events, and wear teal to show your support.
Ovarian cancer is a formidable adversary, but knowledge is power. By understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and the importance of early detection, we can take steps to protect ourselves and our loved ones. Ovarian Cancer Awareness Month serves as a reminder that together, we can make a difference in the fight against this silent killer. So, let’s raise awareness, promote early detection, and work towards a future where ovarian cancer is no longer a threat to women’s health.
For more resources: https://www.cancercare.org/diagnosis/ovarian_cancer